Content
A final type of private equity is a Private Investment in a Public Company (PIPE). A PIPE is a private investment firm’s, a mutual fund’s, or another qualified investors’ purchase of stock in a company at a discount to the current market value (CMV) per share to raise capital. Any asset that is purchased through a secured loan is said to have equity. The lender has the right to repossess it if the buyer defaults, but only to recover the unpaid loan balance. The equity balance—the asset’s market value reduced by the loan balance—measures the buyer’s partial ownership. This may be different from the total amount that the buyer has paid on the loan, which includes interest expense and does not consider any change in the asset’s value.
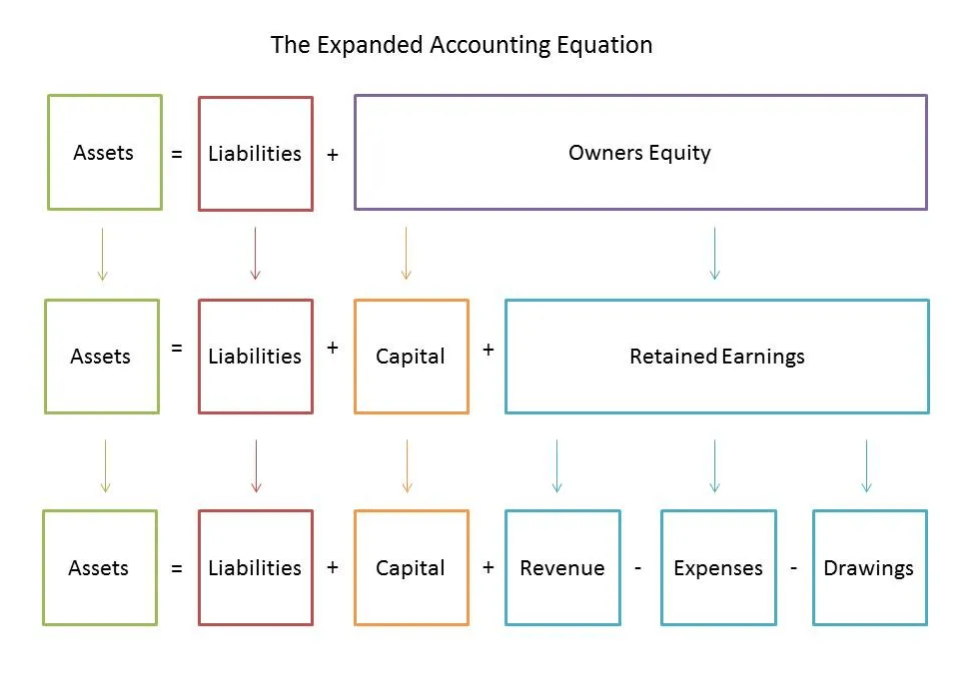
- Shareholder equity is the difference between a firm’s total assets and total liabilities.
- Treasury shares or stock (not to be confused with U.S. Treasury bills) represent stock that the company has bought back from existing shareholders.
- Investors usually seek out equity investments as it provides a greater opportunity to share in the profits and growth of a firm.
- A company’s debt level might be fine for one investor while another might have concerns about the level of debt for the company.
- The value of $65.34 billion in shareholders’ equity represents the amount left for stockholders if Apple liquidated all of its assets and paid off all of its liabilities.
Financial ratio examination uses formulas to gain insight into a business and its operations. Last, of all, inventory signifies the industry’s raw materials, work in growth commodities, and finished commodities. Contingent on the business, the exact makeup of the inventory will alter. Accounts receivables contain the short-term duties owed to the business by its customers. Here, you will be able to learn the importance of both terms for your business.
Equity (finance)
Cash flows or the assets of the company being acquired usually secure the loan. Mezzanine debt is a private loan, usually provided by a commercial bank or a mezzanine venture capital firm. Mezzanine transactions often involve a mix of debt and equity in a subordinated loan or warrants, common stock, or preferred stock.
While some liabilities may be secured by specific assets of the business, others may be guaranteed by the assets of the entire business. If the business becomes bankrupt, it can be required how to calculate total equity to raise money by selling assets. Yet the equity of the business, like the equity of an asset, approximately measures the amount of the assets that belongs to the owners of the business.
What Are the Components of Shareholder Equity?
It is of the owner’s prize in a business of all debts that the business salaries off. Total equity equivalents to total assets reduce the total liabilities and comprise of the sum of money investors. Cash from financing activities includes the sources of cash from investors or banks, as well as the uses of cash paid to shareholders. Financing activities include debt issuance, equity issuance, stock repurchases, loans, dividends paid, and repayments of debt. Unlike the balance sheet, the income statement covers a range of time, which is a year for annual financial statements and a quarter for quarterly financial statements.
Treasury stock appears as a contra-equity balance (an offset to equity) that reflects the amount that the business has paid to repurchase stock from shareholders. Retained earnings (or accumulated deficit) is the running total of the business’s net income and losses, excluding any dividends. In the United Kingdom and other countries that use its accounting methods, equity includes various reserve accounts that are used for particular reconciliations of the balance sheet. Investors can get a sense of a company’s financial well-being by using a number of ratios that can be derived from a balance sheet, including the debt-to-equity ratio and the acid-test ratio, along with many others. The income statement and statement of cash flows also provide valuable context for assessing a company’s finances, as do any notes or addenda in an earnings report that might refer back to the balance sheet. Companies prepare and issue balance sheets annually to inform owners and other stakeholders of the financial position of the company at the end of the fiscal year.
Stockholders’ Equity and Retained Earnings (RE)
First, financial statements can be compared to prior periods to better understand changes over time. For example, comparative income statements report what a company’s income was last year and what a company’s income is this year. Noting the year-over-year change informs users of the financial statements of a company’s health. An often less utilized financial statement, a statement of comprehensive https://www.bookstime.com/articles/adjusting-entries income summarizes standard net income while also incorporating changes in other comprehensive income (OCI). Other comprehensive income includes all unrealized gains and losses that are not reported on the income statement. This financial statement shows a company’s total change in income, even gains and losses that have yet to be recorded in accordance to accounting rules.

For this, we provide a stepwise guide to the one who wants to find the equity on the balance sheet. However, one capitalizes these in the corporation along with salaries that a business accumulates from its operations. Business with a larger portion of equity likened to liabilities typically has a lower risk of insolvency of its inferior debt burden.
Common liability accounts include lines of credit, accounts payable, short-term debt, deferred revenue, long-term debt, capital leases, and any fixed financial commitment. The value of a company’s assets is the sum of each current and non-current asset on the balance sheet. The main asset accounts include cash, accounts receivable, inventory, prepaid expenses, fixed assets, property plant and equipment (PP&E), goodwill, intellectual property, and intangible assets. The cash flow statement (CFS) measures how well a company generates cash to pay its debt obligations, fund its operating expenses, and fund investments. The cash flow statement complements the balance sheet and income statement.
- Managers can opt to use financial ratios to measure the liquidity, profitability, solvency, and cadence (turnover) of a company using financial ratios, and some financial ratios need numbers taken from the balance sheet.
- Operating revenue is the revenue earned by selling a company’s products or services.
- Total equity is the total amount invested by all the shareholders of the company.
- Mezzanine debt is a private loan, usually provided by a commercial bank or a mezzanine venture capital firm.
- To satisfy this requirement, all events that affect total assets and total liabilities unequally must eventually be reported as changes in equity.
- Under the model of a private limited company, the firm may keep contributed capital as long as it remains in business.